Diagnostics at Greenside Vets
All of the techniques below combined allow us to determine the full diagnostic picture of your animal.
Furthermore, the many forms of quantitative analysis enable us to collect data to be used in research studies proving the efficacy of our treatment protocols.
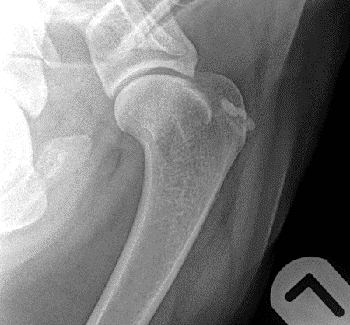 Radiography
Radiography
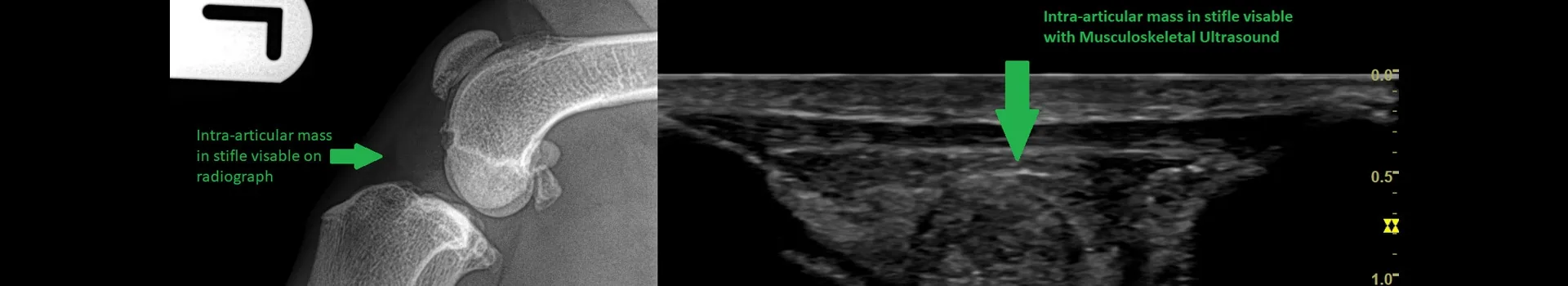
Greenside boasts state-of-the-art radiography equipment. This allows us to do a full assessment of all possible changes. Radiography is the main-stay of OA diagnosis and the first diagnostic tool that is usually recommended to help rule out any other differentials. Radiographic changes that you can visualise in OA include soft tissue swelling, new bone growth and in severe cases quite large deposits of new bone.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSK US)
A detailed non-invasive diagnostic test to confirm soft tissue injuries after localisation to a specific area following a full and thorough clinical exam. It can also be used in certain cases to see thickening of the joint capsule, cartilage defects, joint effusion, bone destruction and inflammation around the bone. MSK US can be used to monitor healing of soft tissues after treatment and/or rehabilitation and can measure cross-sectional areas of tendons over time to monitor response to treatment and resolution of injuries and compare to the opposite limb. At Greenside we use MSK US to monitor and record progression of core lesions in tendons post treatment, the presence of scar tissue and fibre damage, and as a guide for stem cell therapy joint injections.
Digithermal imaging
This allows us to visualise areas of heat or cold within the animal's body. One of the cardinal signs of inflammation is heat so imaging this can help identify areas where inflammation and pain may be occurring. This is particularly useful in identifying spinal issues as nerve problems can result in vasoconstriction and areas of reduced heat in specific patterns on the body which can easily be identified with our extremely sensitive thermal camera.
Force plate analysis
Force platforms are typically based on either piezoelectric or strain gauge technology and are sited inconspicuously in the middle of a walkway which is usually approximately 10m in length. Dogs are led by a handler along the walkway and the limb in question must strike the platform centrally at a controlled velocity (measured force is related to velocity). For each valid measurement, the force-time curve is plotted, and various parameters are derived. The most commonly used parameters are the peak vertical force (PVF) and the vertical impulse (VI); it is documented that limb pain and lameness reduce both PVF and VI. Conversely, effective analgesics and surgical treatments can increase these parameters in the index limb in lame dogs.
Stance analysis
This is a flat platform mat on which the patient stands with one foot in each quadrant. It is a tool to enable practitioners to quickly get objective measurements to show how the patient is weight bearing. The data provides four averaged numbers that show the percentage of the patient’s weight being placed on each limb. It can also be used to provide stability and centre of gravity data. The ideal percentages are 30% for each forelimb and 20% for each hind limb.
Goniometry
Goniometry is the process of measuring a joint's full range of motion. A goniometer is used to measure the angle of full flexion and full extension of the limb, and this is recorded. This can be compared to breed averages as well as compared throughout a treatment program to ensure beneficial changes are being achieved.
 Gulick muscle mass
Gulick muscle mass
This is how we quantify muscle mass. Using a Gulick tape measure, which has a pressure gauge allowing all practitioners to use the same pressure whilst measuring, makes the results more accurate.
Pressure algometry
We commonly use a pressure algometer at Greenside which is used to measure the amount of pressure per square inch an animal can sustain before exhibiting a pain response. This is used to quantify back pain.
Needle arthroscopy
This is a very small camera that can be used to visualise the inside of joints and tendons/ligaments to assess the extent of damage or obtain a definitive diagnosis. It is a relatively non-invasive tool used to directly visualise a potential injury or disease process within the body.